The highlights:
- Dysphagia has an outsized impact on older adults within nursing homes, with 75% experiencing some degree of dysphagia symptoms.
- Biofeedback could play a role in helping elevate dysphagia treatment.
- ACP’s Synchrony Dysphagia Solutions offers powerful sEMG biofeedback for effectively treating and managing dysphagia in older adults.
June is National Dysphagia Awareness Month, a time to raise awareness around a swallowing disorder that impacts up to 33% of older adults and 75% of nursing home residents.1 Widely defined as “swallowing difficulties,” dysphagia is a serious condition that can increase the risk for other illnesses, malnutrition, and mortality. Despite the prevalence and impact of dysphagia, particularly among older adults, broader discussions have been happening around the need for standardization and unification around the definition, screening, assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and management of this common disorder. Biofeedback could play a role in helping elevate dysphagia treatment.
Exploring the Benefits of Biofeedback in Dysphagia Care
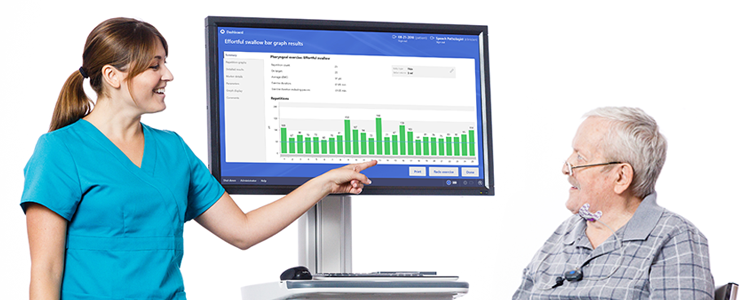
In conjunction with traditional Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP) therapy techniques such as diet modification, compensation strategies, and direct swallowing exercises, biofeedback provided by technologies like Synchrony Dysphagia Solutions becomes an asset in treating dysphagia in older adults. Using real-time data about swallowing function, clinicians can improve the effectiveness of treatment.
Generally speaking, biofeedback in dysphagia treatment can help with:
- Objective Measurement: Biofeedback can provide objective measurements of swallowing function, such as timing of swallow events, and coordination of swallow movements. This objective data can help SLPs track progress over time.
- Customized Therapy: With biofeedback, clinicians can better tailor dysphagia therapy to each patient’s specific needs. By identifying areas of swallowing impairment through instrumental assessments, SLPs can implement targeted exercises to improve swallowing strength and efficiency.
- Immediate Feedback: Real-time feedback during swallowing exercises enables patients to adjust their swallowing patterns in response to visual or auditory cues. This immediate feedback helps patients understand their swallowing function and learn to adapt accordingly.
- Motivation and Engagement: Biofeedback, especially when gamified through virtual reality, can enhance patient engagement in their therapy. Seeing improvements in swallowing function on a biofeedback display can be highly motivating for patients, encouraging them to continue with their therapy regimen.
- Standardized Protocols: Biofeedback can help standardize treatment protocols for dysphagia by providing a common framework for assessment and intervention. By using standardized measurement techniques and protocols, SLPs can ensure consistency in the evaluation and treatment of their patients with dysphagia. This ultimately enhances the quality of care provided to patients and promotes evidence-based practice in dysphagia management.
Leverage Biofeedback with Synchrony Dysphagia Solutions by ACP®
Designed specifically for SLPs and their patients, ACP’s Synchrony Dysphagia Solutions combines surface electromyography (sEMG) biofeedback and patterned electrical stimulation (PENS) with a virtual environment to engage patients in fun, interactive swallowing and speech exercises. It enables therapists and patients to visualize swallowing and speech activity with instant biofeedback that can help improve the accuracy and effectiveness of dysphagia treatment, drive behavioral changes, and lead to better patient outcomes.
Unlock Advanced Dysphagia Care with Synchrony
Are you interested in incorporating biofeedback technologies into your dysphagia program? Learn how Synchrony can help.
- Thiyagalingam, S., Kulinski, A., Thorsteinsdottir, K., Shindelar, K., & Takahashi, P. (2021). Dysphagia in Older Adults. Thematic Review on Aging. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 96(2), 488-497. Retrieved [2024, June 5] from https://www.mayoclinicproceedings.org/article/S0025-6196(20)30902-2/pdf ↩︎
MRK-BLOG-006
June is National Dysphagia Awareness Month, a time to raise awareness around a swallowing disorder that impacts up to 33% of older adults and 75% of nursing home residents. Widely defined as “swallowing difficulties,” dysphagia is a serious condition that can increase the risk for other illnesses, malnutrition, and mortality. Despite the prevalence and impact of dysphagia, particularly among older adults, broader discussions have been happening around the need for standardization and unification around the definition, screening, assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and management of this common disorder. Learn how biofeedback could play a role in elevating dysphagia treatment.


